The European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing (EIP on AHA)
The European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing (EIP on AHA), set up in 2012, gathers stakeholders at EU, national and regional level from the public and
private sector across different policy areas. Together they share knowledge and expertise on common interests and engage in activities and projects to find innovative solutions
that meet the needs of the ageing population.
Under the framework of the EIP on AHA, the Action Group on integrated care works to improve the quality of life and health outcomes of older people with chronic conditions
and reduce unnecessary hospitalisations by promoting new health care models based on a better integration of the different levels of health and care services.
ND-02-14-817-EN-N
https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/eipaha/
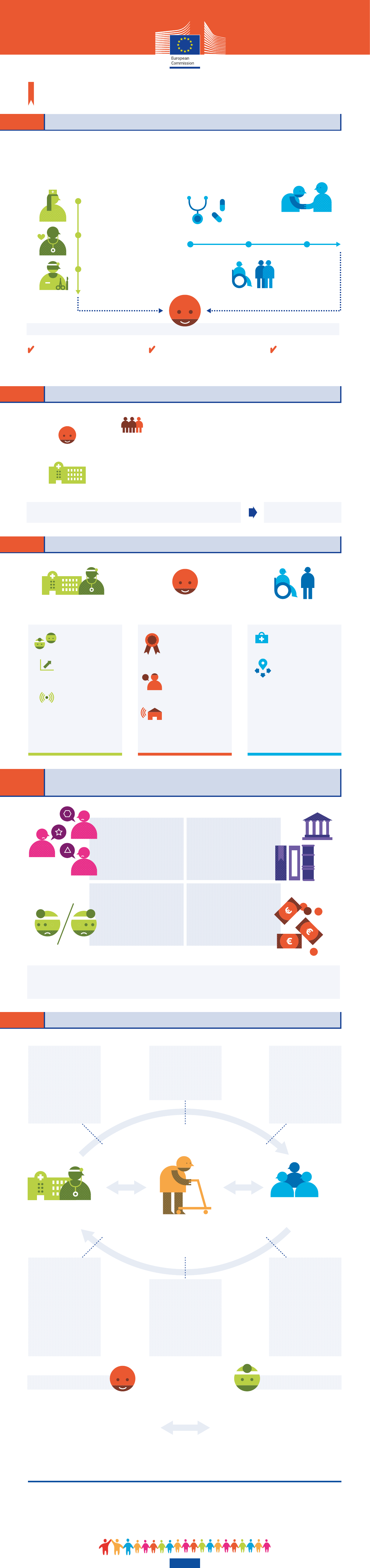
WHAT IS INTEGRATED CARE?
Integrated care and chronic diseases management
A European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing priority
Integrated care is the coordination of care:
Some relevant features:
WHY DO WE NEED INTEGRATED CARE?
VERTICALLY, ACROSS THE
LEVELS OF HEALTH CARE:
PRIMARY CARE
First contact and principal point
of continuing care (e.g. general
practitioners, nurses, pharmacists)
SECONDARY CARE
Provided by specialists
(e.g. cardiologist,
gastroenterologist)
TERTIARY CARE
Hospitals, highly specialised
health service (e.g. cardiac surgery,
cancer treatment)
HORIZONTALLY, ACROSS DIFFERENT
TYPES OF CARE DELIVERY:
COMMUNITY CARE
Including informal care provided by
the family and non-profit sector
Patient-centred approach and active
involvement of the patients in understanding
and managing their own diseases (patient
empowerment)
Move from institutional
to community / home
based care
2 out of 3 people in retirement age have at least
two chronic conditions
of healthcare costs are
spent on chronic diseases
It is necessary to offer alternative care models to improve quality
of life, health care and reduce avoidable hospitalisations / costs
Integrated care model
FOR HEALTH SYSTEMS
FOR PATIENTS
70%
of GDP: Public
spending on health
9%
of healthcare costs are
dedicated to hospital care
41%
of GDP: Projected
increase by 2060
+1.5%
Shiſt from reactive service delivery (aſter
adverse health events, e.g. a cardiac arrest) to
preventive and proactive care (prevent and
manage chronic conditions, e.g. maintain healthy
blood pressure / cholesterol level)
HEALTH CARE
SOCIAL CARE
PATIENT
WHAT ARE THE CURRENT BARRIERS TO THE IMPLEMENTATION
OF INTEGRATED CARE MODELS?
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF INTEGRATED CARE MODELS?
Higher support in
providing care
Easier navigation
through health system
FOR HEALTH AND SOCIAL
CARE SYSTEMS
FOR PATIENTS FOR CARE GIVERS
Better coordination
among health and social
care professionals
Higher efficiency,
improved healthcare
processes, supported by IT
New organisational
models and use of
technologies for remote
care (e.g. at home or at
work)
Better quality and more
timely care, easier
navigation within the
healthcare system
Personalised approach,
involvement in the
management and
decision about their
diseases
Higher autonomy and
possibility to remain at
home thanks to the use
of remote monitoring
services
Health and social care
sectors oſten operate
in silos
Current solutions are
proprietary (i.e. belong to a
single provider) and cannot
be extended to other needs
or target users, leading to
market fragmentation
Legal and regulatory
uncertainties
(i.e. data protection)
Lack of financial
incentives
(public procurement / lack of
innovative reimbursement
models)
HOW CAN IT BE IMPLEMENTED?
HEALTH
SYSTEM
Clinical
information
systems
Organisation
of healthcare
Decision
support
Delivery
system design
WHAT IS IT?
Better coordination among
healthcare organisations
HOW?
Ensure political leadership and
engagement of local actors to
strengthen cooperation
WHAT IS IT? To enable
older people to remain longer
at home
HOW?
Through legal framework
for integrating health and
social care, financial support,
procurement of remote
monitoring solutions
WHAT IS IT? More efficient
sharing of data (disease
information, patient records,
health management methods)
HOW? Use IT tools to share:
- electronic health records of
citizens across care institutions
- electronic files on
pharmaceutical records
to avoid medical interactions
and prescription duplication
WHAT IS IT? Support the
change management in regions
towards integrated care models
HOW?
- Use of ICT tools to enable
coordination
- Funding delivered on the basis
of performance and quality
- Identify individuals with higher
health risks and dedicate
services to them
WHAT IS IT? Care and
encouragement provided to old
people and their families to help
them manage their disease
HOW?
Through tele-medicine
services, rehabilitation centres,
emotional support
WHAT IS IT? Tools to help
doctors and patients to navigate
together through the system
and to better tailor interventions
to their patients’ needs
HOW?
- Tailored interventions based
on patients health profile and
patient specific data
(risk stratification tools)
- Guidelines to set up
personalised and better
coordinated care pathways
Patients
PRODUCTIVE
INTERACTION
WHAT IS IT?
Patients are well informed and empowered
to manage their disease
HOW?
- Volunteers, self-help groups
- Accessible information, improved health literacy
- Mobile and web platforms to trigger positive changes
in patient behaviour and raise awareness
- Engagement in decision-making
WHAT IS IT?
Health professionals receive more comprehensive
information and have tools for decision-making
HOW?
- ICT education for health workforce
- Structures for professional cooperation and teamwork
- Share of knowledge and information
Inspired by the model set up by the MacColl Institute for healthcare innovation
COMMUNITY
Resources
and policies
Self-management
support
Health professionals
The European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing (EIP on AHA) supports private
and public actors across the EU to implement integrated care models.
Target: implementation of integrated care programmes in 20 regions by 2020.
 Scroll
Scroll